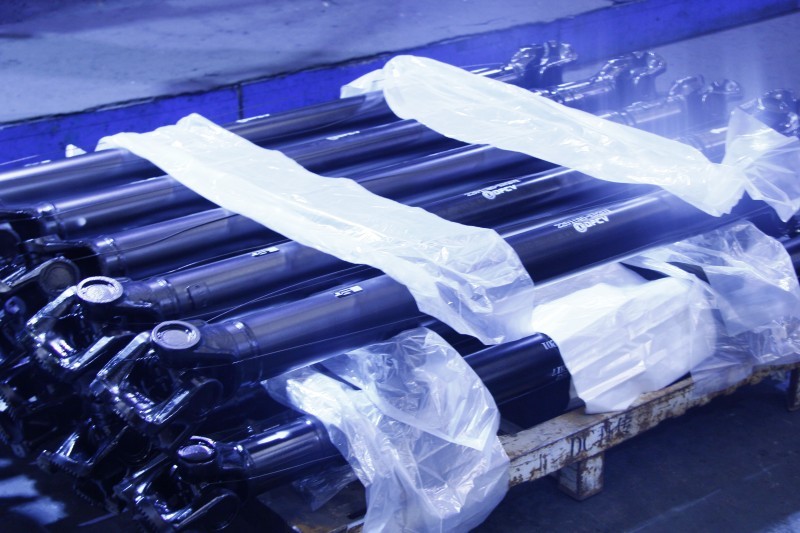
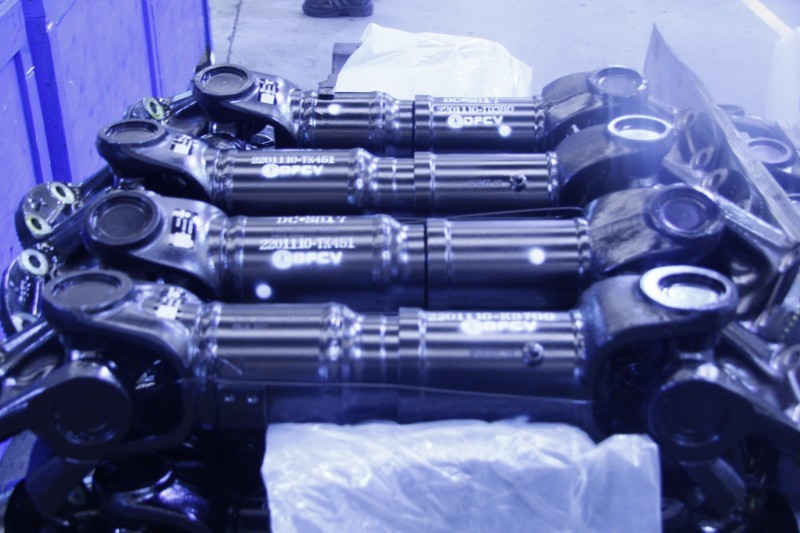
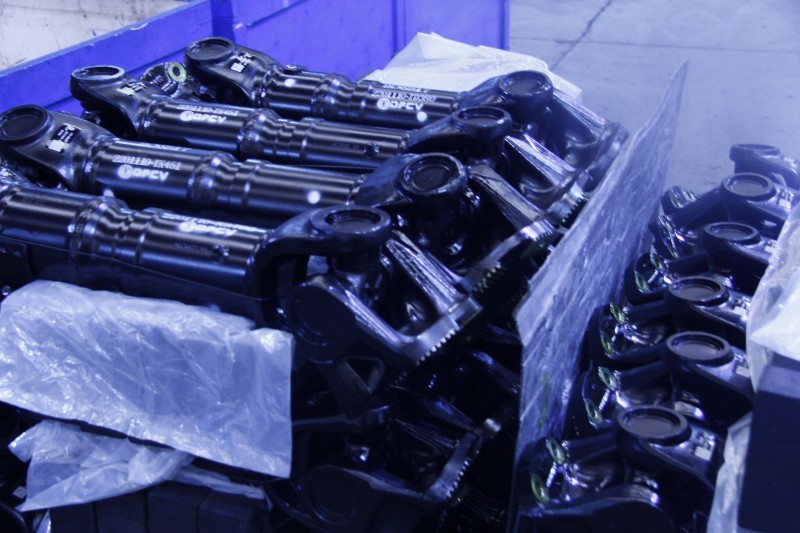
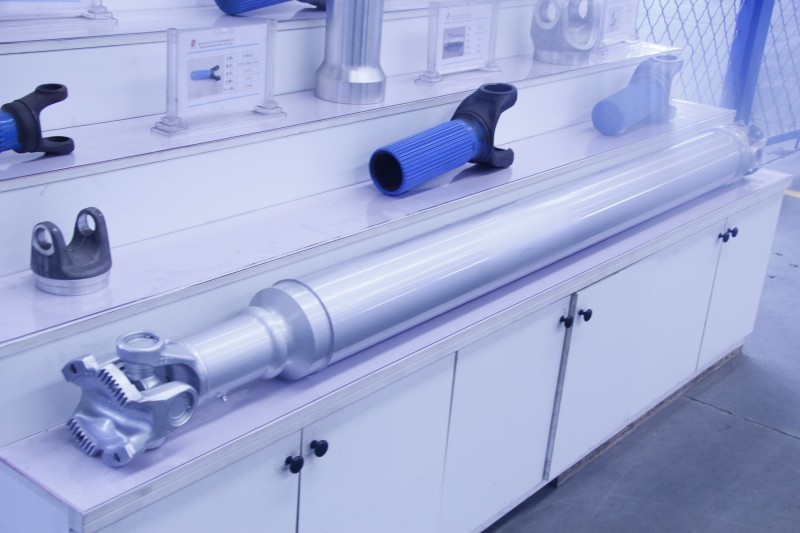
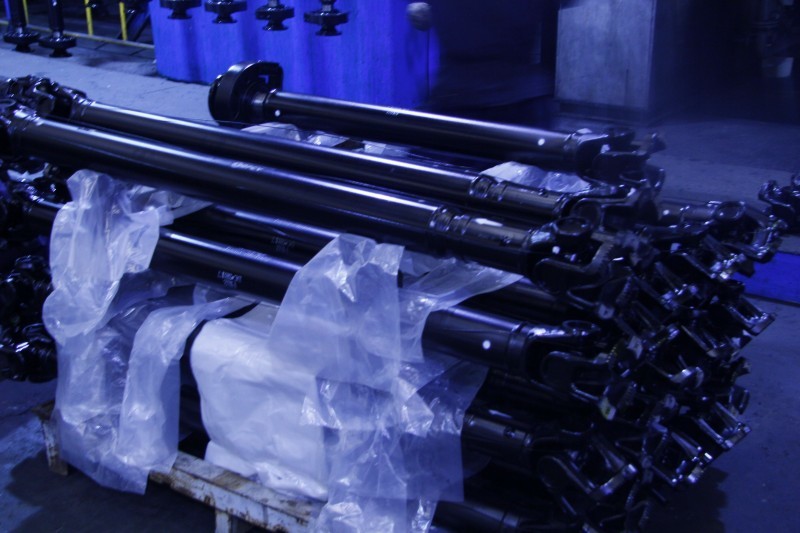
Steel driveshaft (rear)
Category:
The driveshaft assembly is a crucial component in a vehicle's drivetrain, responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the drive axle via the transmission.
Contact:
Product Details
Driveshaft Assembly It is an important component in the power transmission system of an automobile, responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the differential gear via the transmission. Below is a detailed explanation of the driveshaft assembly.
1. Structure
Universal Joint
The universal joint is a key component of the driveshaft assembly, effectively transmitting power even at different angles. Common universal joints include the cross-type universal joint and the constant-velocity universal joint.
The cross-type universal joint has a simple structure, mainly consisting of a cross shaft, universal joint yoke, needle roller bearings, etc. It can operate at large angles, but unequal velocity occurs during transmission, and the angular velocity of the input and output ends are not equal. This universal joint is usually placed at both ends of the driveshaft, and the effect of unequal velocity is reduced by a specific arrangement method.
The constant-velocity universal joint is mainly used for the half-shafts of front-wheel-drive vehicles and can maintain constant velocity during operation. The structure of the constant-velocity universal joint is relatively complex, and there are various forms, such as ball joint type and ball fork type. Taking the ball joint type constant-velocity universal joint as an example, there are spherical outer planetary gears and inner planetary gears inside, and steel balls roll between them, realizing constant-velocity transmission by the rolling of the steel balls. This structure maintains stable power transmission even when the angle between the half-shaft and the wheel changes greatly during steering.
Shaft Tube
The shaft tube is the main part of the driveshaft and has a hollow cylindrical tubular structure. The main role of the shaft tube is to connect the universal joints at both ends and provide a stable path for power transmission. The shaft tube is usually made of high-strength steel and has sufficient strength and rigidity to withstand torque.
The length of the shaft tube is designed according to the vehicle's wheelbase and power transmission path. Vehicles with longer wheelbases or longer power transmission distances (such as some pickup trucks and off-road vehicles) have relatively longer shaft tubes. Strict requirements are placed on the thickness and material quality of the shaft tube to ensure its stability during operation.
Telescopic Coupling and Intermediate Support (Some Driveshafts)
The telescopic coupling is used to compensate for changes in the length of the driveshaft. During vehicle operation, factors such as the suspension system and wheel bounce cause changes in the distance between the transmission and the differential gear. The telescopic coupling expands and contracts within this range of distance changes, ensuring that the driveshaft operates normally. Telescopic couplings generally adopt a spline structure, with the inner spline and outer spline meshing with each other, and the length is adjusted by the sliding of the spline.
The intermediate support is a support device installed in the center of the driveshaft, mainly supporting the driveshaft and preventing large vibrations during high-speed rotation. The intermediate support is generally a bearing device with a rubber elastic element. The rubber elastic element absorbs the vibrations and shocks generated during the operation of the driveshaft, and the bearing ensures that the driveshaft rotates smoothly. The installation position and number of intermediate supports are determined by the length and operating conditions of the driveshaft. Generally, intermediate supports are equipped when the driveshaft is too long or the torque is large.
2. Operating Principle
Power Transmission Process
When the engine outputs power, the transmission first performs shifting and torque conversion. The output shaft of the transmission is connected to the driveshaft via a universal joint. The power is transmitted from the output shaft of the transmission to the universal joint of the driveshaft, and the universal joint transmits the power to the shaft tube. The shaft tube transmits the power to the other universal joint, and finally, the power is transmitted to the input shaft of the differential gear via the universal joint.
In this process, the universal joint can adapt to changes in the angle between the transmission and the differential gear. For example, when the vehicle is traveling on uneven terrain, the wheels bounce up and down, and the relative position between the transmission and the differential gear changes, but the universal joint can ensure continuous power transmission within this range of angular change.
Our company has subsidiaries specializing in transmission shafts, aluminum alloy forging, cast steel, and precision casting. Our main products include transmission shaft assemblies and parts, forgings, large castings, precision castings, and aluminum forgings. We serve the automotive, construction machinery, agricultural machinery, and rail transportation industries.
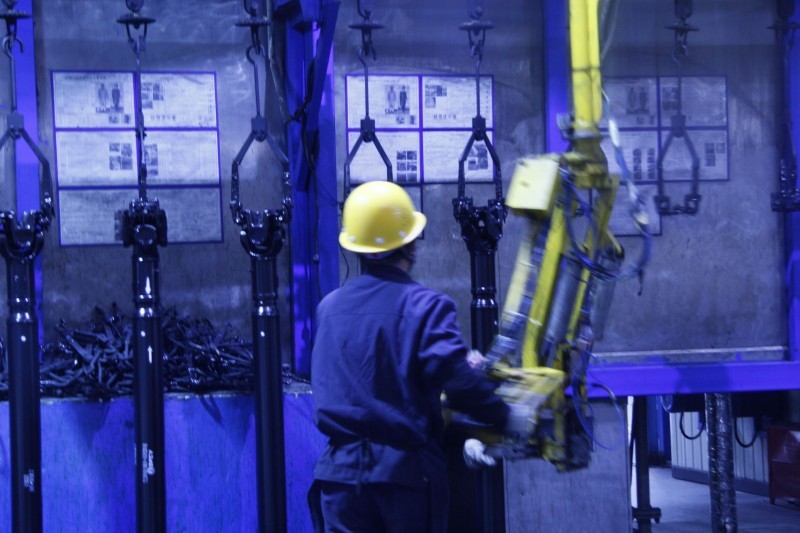
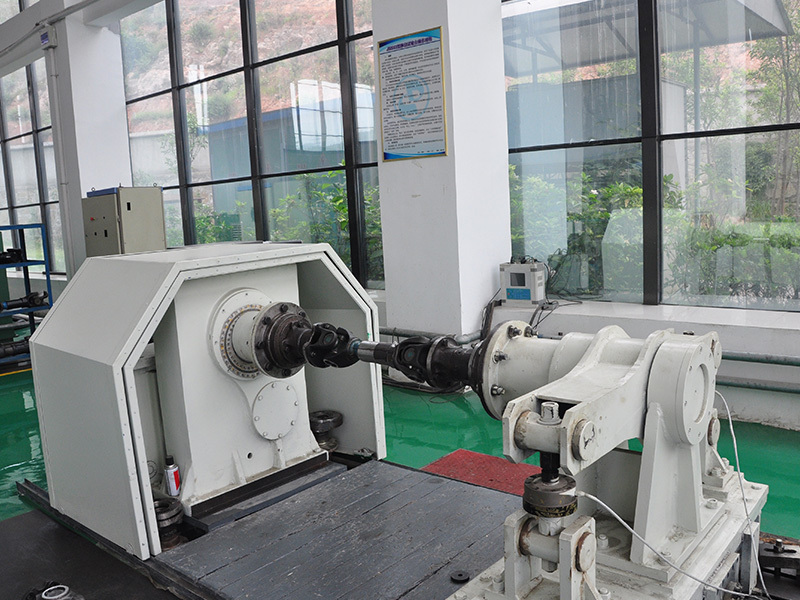
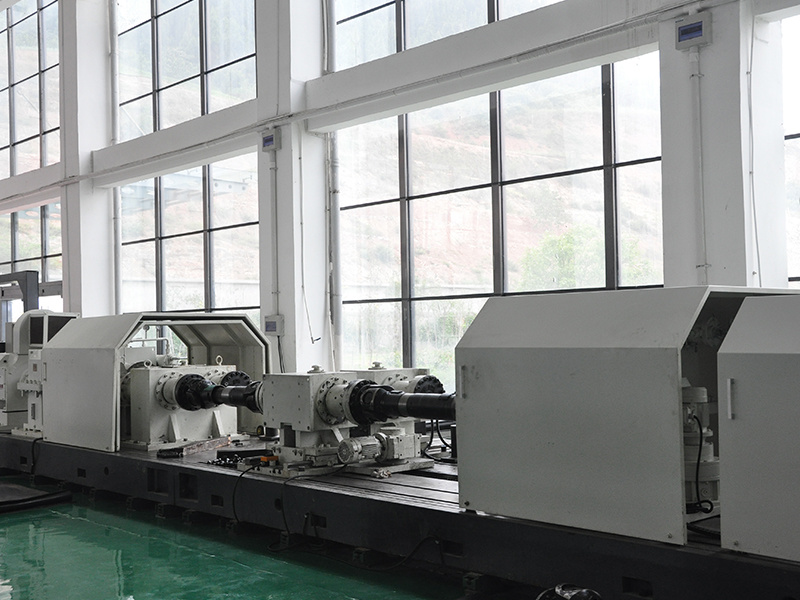
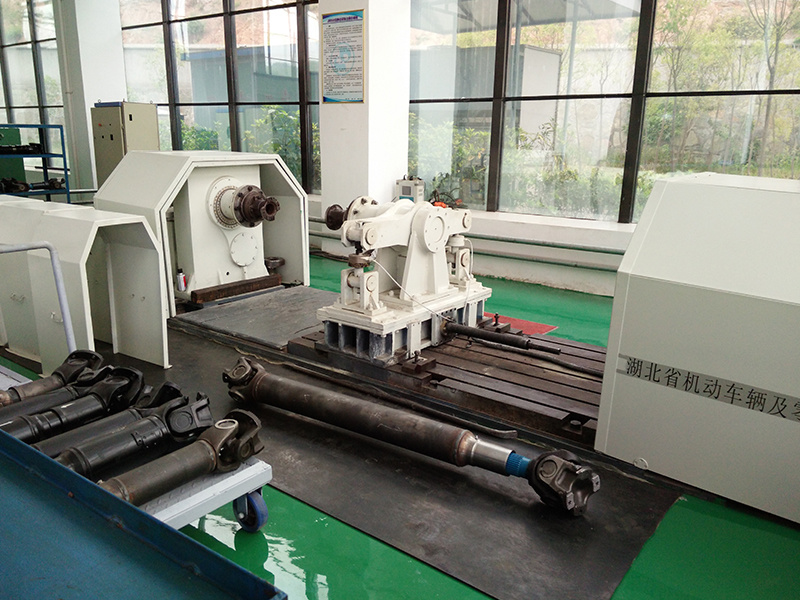
Production Capacity

Engineering video 3

Engineering video 2

Factory video
Quality Inspection
Related Products
Contact Us
Once we receive your message, we will contact you immediately and prepare a surprise for you.
Contact
Address:No. 226, Shuidu Avenue, Danjiangkou Economic Development Zone